
DevTools Extension
get_it includes a DevTools extension that lets you visualize and inspect all registered objects in your running Flutter app in real-time.
Key features:
- ✅ View all registrations - See every object registered in get_it across all scopes
- ✅ Inspect instance state - View the toString() output of created instances
- ✅ Track registration details - Type, scope, mode, async status, ready state, creation status
- ✅ Real-time updates - Automatically refreshes when registrations change (with debug events enabled)
Setup
1. Enable Debug Events
In your app's main.dart, enable debug events before running your app:
void main() {
GetIt.instance.debugEventsEnabled = true;
// ... configure your dependencies
configureDependencies();
runApp(MyApp());
}Why Enable Debug Events?
When debugEventsEnabled is true, get_it sends events to DevTools whenever registrations change, allowing the extension to automatically update. Without this, you'll need to manually refresh the extension to see changes.
Debug Mode Only
The DevTools extension only works in debug mode. In release builds, the extension is not available and debug events have no effect.
2. Run Your App in Debug Mode
flutter run3. Open DevTools in Browser
The get_it extension currently only works in the browser-based DevTools, not in IDE-embedded DevTools.
When you run your app, Flutter will display a message like:
The Flutter DevTools debugger and profiler is available at: http://127.0.0.1:9100Open that URL in your browser.
4. Enable the Extension
- In DevTools, click the Extensions button (puzzle piece icon) in the top right corner
- Find the
get_itextension in the list and enable it - The "get_it" tab will appear in the main DevTools navigation
5. Open the get_it Tab
Click on the "get_it" tab to view all your registrations.
Understanding the Registration Table
The DevTools extension displays all registered objects in a table with the following columns:
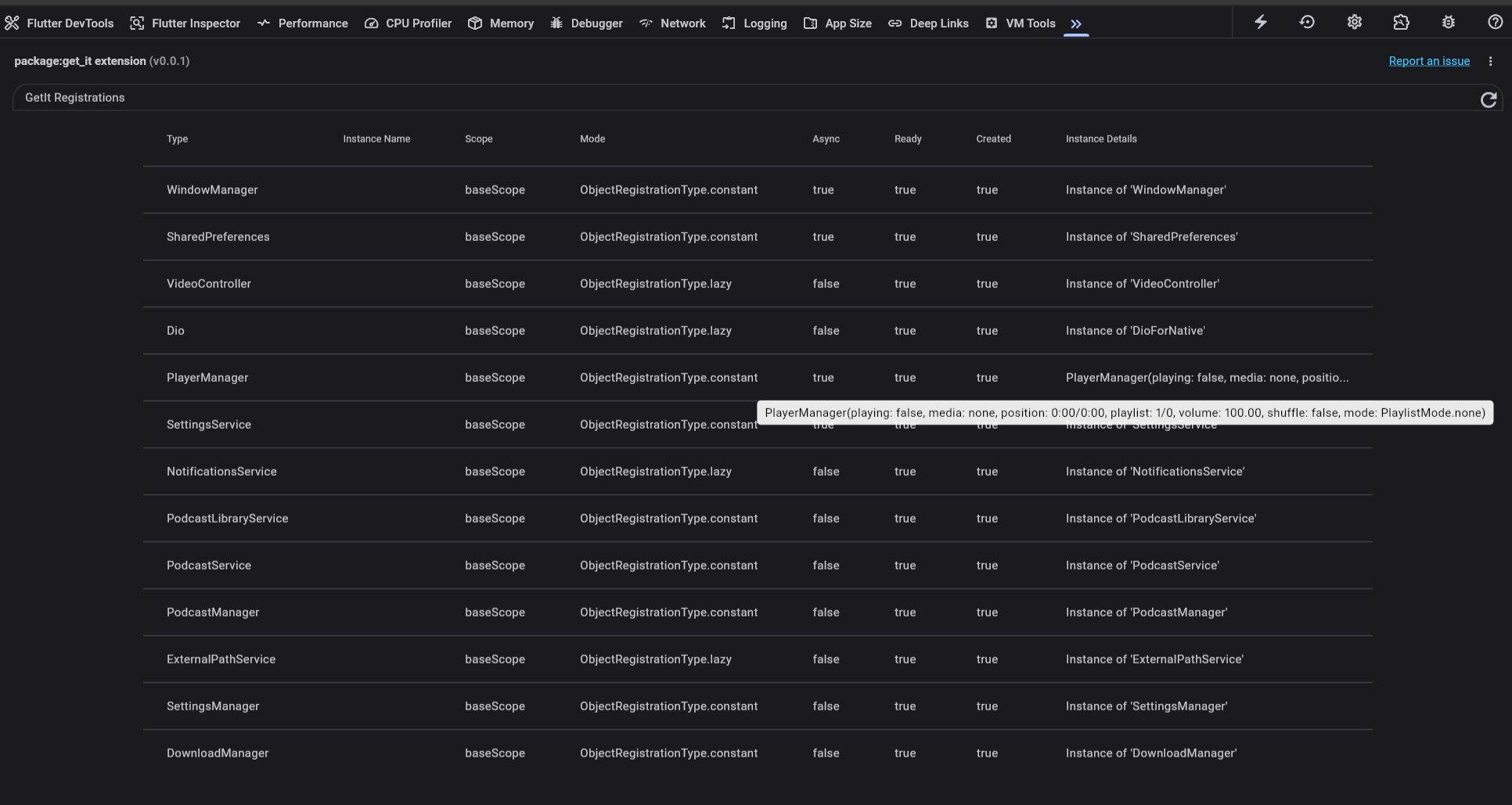 The get_it DevTools extension showing all registered objects in a running app
The get_it DevTools extension showing all registered objects in a running app
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The registered type (class name) |
| Instance Name | The instance name if using named registrations, otherwise empty |
| Scope | The scope this registration belongs to (e.g., baseScope for the default scope) |
| Mode | The registration type: constant (singleton), lazy (lazy singleton), alwaysNew (factory), or cachedFactory |
| Async | Whether this is an async registration (true for registerSingletonAsync and registerLazySingletonAsync) |
| Ready | For async registrations, whether the initialization is complete |
| Created | Whether the instance has been created (false for lazy registrations that haven't been accessed yet) |
| Instance Details | The toString() output of the instance (if created) |
Making Instance Details Meaningful
By default, Dart's toString() only shows the type name and instance ID (e.g., Instance of 'UserRepository'). To see meaningful details in the DevTools extension, override toString() in your registered classes:
class UserRepository {
final String userId;
final bool isAuthenticated;
UserRepository(this.userId, this.isAuthenticated);
@override
String toString() {
return 'UserRepository(userId: $userId, isAuthenticated: $isAuthenticated)';
}
}Now in DevTools, you'll see:
UserRepository(userId: user123, isAuthenticated: true)Tips for Good toString() Implementations
- ✅ Include key state - Show the most important properties that help you understand the object's current state
- ✅ Keep it concise - Long strings are hard to read in the table. Stick to the essential information
- ✅ Use descriptive names - Make it obvious what each value represents
- ✅ Include enum states - If your object has states or modes, include them
Example for a media player:
class PlayerManager {
bool isPlaying;
String? currentTrack;
Duration position;
Duration duration;
@override
String toString() {
final posStr = '${position.inMinutes}:${(position.inSeconds % 60).toString().padLeft(2, '0')}';
final durStr = '${duration.inMinutes}:${(duration.inSeconds % 60).toString().padLeft(2, '0')}';
return 'PlayerManager('
'playing: $isPlaying, '
'track: ${currentTrack ?? 'none'}, '
'position: $posStr/$durStr'
')';
}
}This shows: PlayerManager(playing: true, track: My Song, position: 2:34/4:15)
Refreshing the View
- With debug events enabled: The view automatically updates when registrations change
- Without debug events: Click the Refresh button in the extension to manually update the view
- Manual refresh: You can always click Refresh to ensure you're seeing the latest state
Troubleshooting
The get_it tab doesn't appear
- ➜ Make sure you're using browser-based DevTools, not IDE-embedded DevTools
- ➜ Verify the extension is enabled in the Extensions menu (puzzle piece icon)
- ➜ Ensure your app is running in debug mode
The extension shows no registrations
- ➜ Make sure you've actually registered objects in your app
- ➜ Click the Refresh button to manually update the view
- ➜ Verify you're looking at the correct DevTools instance for your running app
The extension doesn't auto-update
- ➜ Check that
debugEventsEnabled = trueis set before any registrations - ➜ Use the manual Refresh button if auto-updates aren't working
Use Cases
During Development
- Verify registrations - Ensure all required services are registered at startup
- Debug initialization - Check which async singletons are ready
- Inspect state - View the current state of your services and models
- Understand scopes - See which objects belong to which scope
During Testing
- Verify test setup - Ensure mocks are registered correctly
- Debug flaky tests - Check if objects are being created multiple times
- Scope isolation - Verify that test scopes are working as expected
During Debugging
- Track down bugs - Inspect service state when bugs occur
- Verify lifecycle - Check if lazy singletons are created when expected
- Monitor changes - Watch how registrations change as you navigate your app
Learn More
- Testing with get_it - Learn how to test your get_it registrations
- Scopes - Understand how scopes work
- Async Objects - Learn about async initialization
- Official Flutter DevTools Documentation